
A warning has been issued over a substance widely available across the US but lacking FDA approval. It affects opioid receptors and has been linked with overdoses and deaths, earning it the nickname ‘gas station heroin’.
As the opioid crisis the US shows no signs of abating, there’s a risk that opioid addicts may target products containing the substance which are being sold under the guise of wellness nootropics, otherwise known as mood and clarity enhancers, that are being sold in the US without FDA approval.
Often labelled as dietary supplements, these products can get around FDA regulation and thus don’t get the clinical or commercial scrutiny their effects necessitate.
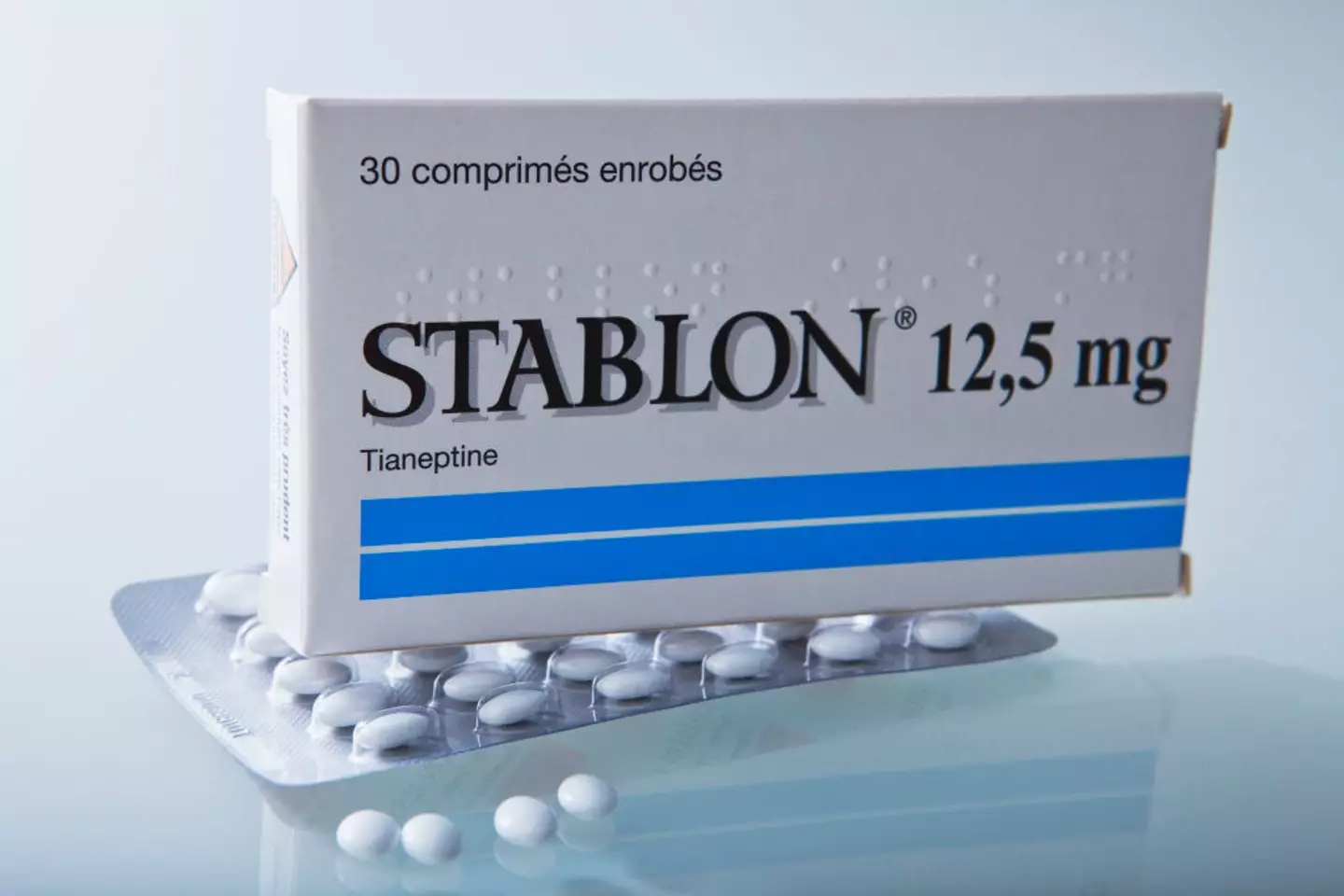
The substance, tianeptine, was developed in the 1960s by French researchers, and it was approved there for use in depression treatment in the 80s. It has never had medical approval in the US, however.
Advert
Tianeptine has a similar chemical structure to tricyclic antidepressants which have been superseded by modern options like sertraline and other SSRIs.
However, while it resembles some older antidepressants, it behaves differently in the human body. While antidepressants generally increase serotonin levels in the brain, tianeptine acts on the glutamate system that plays a key role in learning and memory.
It’s sold in some European, Asian and Latin American countries under prescription, branded as Coaxil and Stablon among others.
Since its approval for use as an antidepressant over 40 years ago, researchers have found that tianeptine actually impacts upon mu-opioid receptors in the brain. These receptors are the same that bind with opioids like morphine and heroin.
While the opioid effect at prescription doses is minor, larger doses can result in similar effects to heroin including euphoria and sedation. It can also give rise to dependence and addiction.
Data from US poison control data details how tianeptine exposure-related calls jumped by more 500% between 2018 and 2023. In 2024, tianeptine was linked with over 300 poisoning incidents.
Tianeptine also goes unnoticed in standard toxicology analyses, meaning its prominence is likely underreported.
Some who have taken products containing the substance have reported opioid-style withdrawal symptoms, including anxiety, insomnia, tremors, muscular aches and diarrhoea.
In its warning about the substance, the FDA said:
“Tianeptine is not approved as a drug in the U.S. Although other countries have approved tianeptine to treat depression and anxiety, some have restricted how tianeptine is prescribed or dispensed, or warned of possible addiction.

“In the U.S., reports of bad reactions and unwanted effects involving tianeptine are increasing. Annual poison control center cases involving tianeptine exposure, as reported by the National Poison Data System, have increased nationwide, from 4 cases in 2013 to about 350 cases in 2024.
It continued: “Cases described in medical journals, in calls to U.S. poison control centers and in reports to the FDA suggest that tianeptine has a potential for abuse. People with a history of opioid use disorder or dependence may be at particular risk of abusing tianeptine.”
